1. 스택
LIFO(Last In First Out)이라는 개념을 가진 선형 자료구조- 나중에 들어간 것이 먼저 나온다.
- 바닥이 막힌 상자를 생각하면 편하다.
- e.g.) 프링글스 통
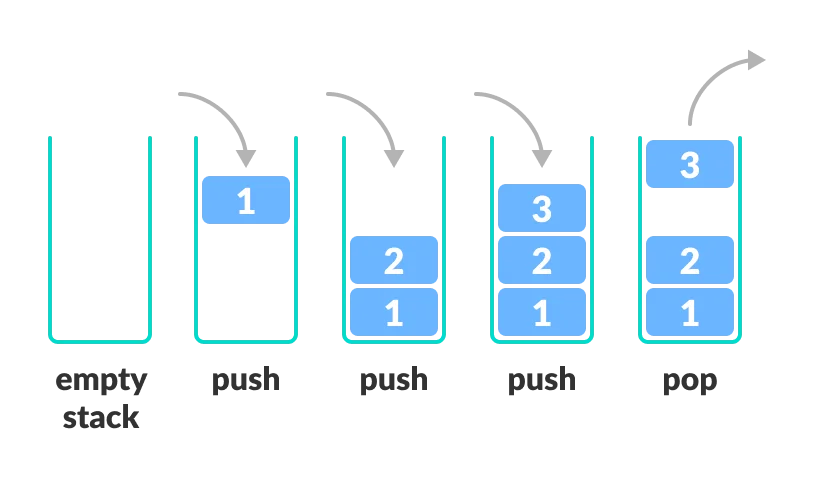
- 한쪽 끝에서 삽입, 삭제가 이루어지는 후입선출(LIFO, Last in First Out) 구조를 가진다.
- 스택에 데이터가 삽입될 위치를 Top이라고 한다.
1.1 스택의 기본 연산
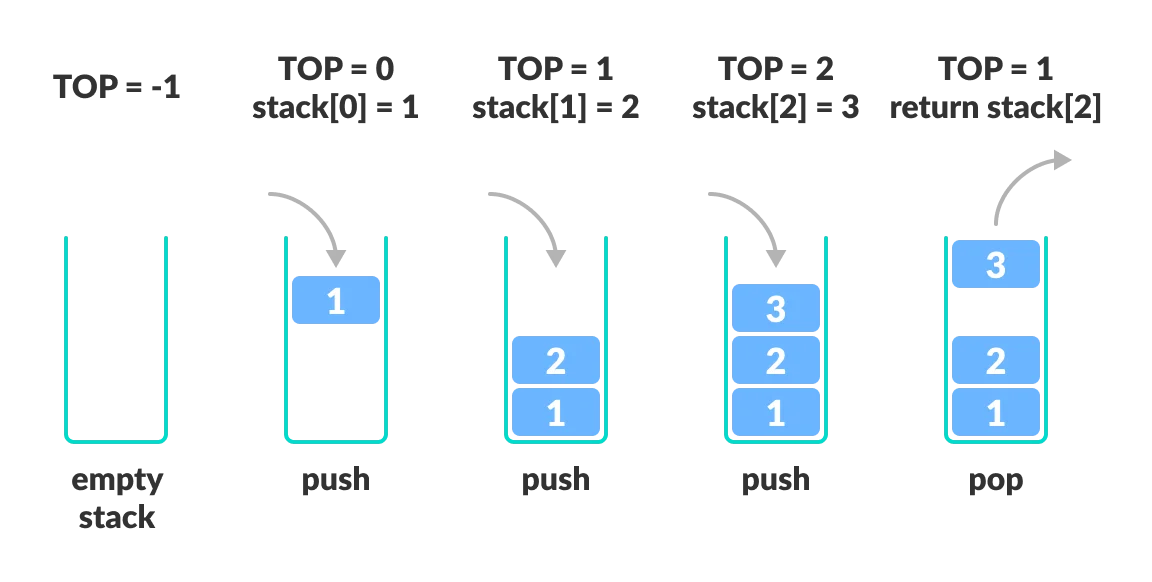
push(data): 스택의 top에 데이터를 삽입pop: 스택의 top에 위치한 요소를 제거isEmpty: 스택이 비어있는지 확인isFull: 스택이 꽉 찼는지 확인peek or top: 스택의 top에 위치한 요소를 반환
1.1 스택 메모리
1function sum(a, b) {2return a + b3}4function print(value) {5console.log(value)6}7print(sum(5, 10))
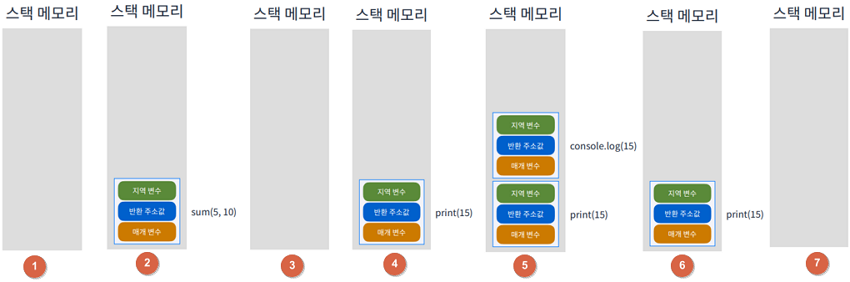
- 스택 메모리는 함수가 호출되면, 생성되는
지역변수, 변환 주소값, 매개변수가 저장되는 메모리 영역입니다. - 가장 안쪽에 위치한 sum(5, 10)함수가 실행됨
- sum()함수 실행이 종료되어, 스택 메모리에서 pop이 수행되며 제거가 됩니다.
- print(15)가 실행됩니다.
- print() 내부에는 console.log()가 있어, 스택 메모리에 다시 쌓이게 됩니다.
- console.log() 출력을 마쳤다면, 스택 메모리에서 제거가 됩니다.
- print()도 함수 호출이 완료되면서, 스택 메모리에서 제거가 됩니다.
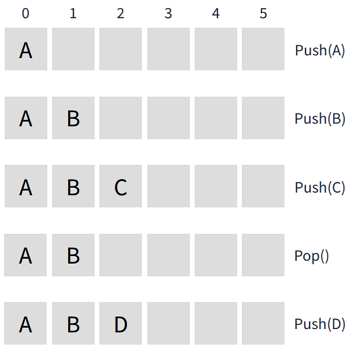
1.2 Array로 표현하기
Stack을 Array로 표현할 수 있다.
1.3 Linked List로 표현하기
Stack을 Linked List로 표현할 수 있다.
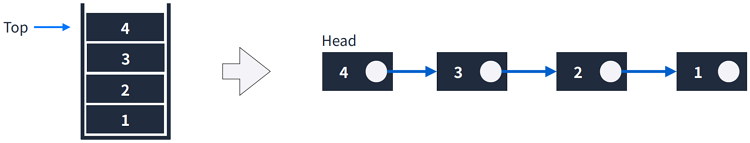
2. 구현
2.1 Array로 구현
1const stack = []23// push4stack.push(1)5stack.push(2)6stack.push(3)7console.log(stack) // [ 1, 2, 3 ]89// pop10stack.pop()11console.log(stack) // [ 1, 2 ]1213console.log(stack[stack.length - 1]) // 2
2.2 Linked List로 구현
1class Node {2// 생성자: new 키워드로 객체를 생성할때 호출되는 함수3constructor(value) {4this.value = value5this.next = null6}7}89class Stack {10// 생성자: new 키워드로 객체를 생성할때 호출되는 함수11constructor() {12this.top = null13this.size = 014}15// 추가16push(value) {17const node = new Node(value) // 입력받은 값으로 새 노드 생성18node.next = this.top // 새로 생성한 노드의 다음은 실행노드의 top을 가르킴19this.top = node // 실행노드의 top은 노드를 가르킴20this.size += 121}22// 삭제23pop() {24const value = this.top.value // 실행노드의 top의 value를 변수로25this.top = this.top.next // 실행노드의 top의 next를 top으로26this.size -= 127return value28}29size() {30return this.size31}32}3334const stack = new Stack()35stack.push(1)36stack.push(2)37stack.push(3)38console.log(stack.pop()) // 339stack.push(4)40console.log(stack.pop()) // 441console.log(stack.pop()) // 2
3. 스택 실습 : 올바른 괄호
3.1 문제
3.2 풀이
push '('와pop ')'을 한 번씩 해서 빈 배열이 되어야 함- 올바른 괄호 :
(())() - 올바르지 않은 괄호 :
(()(
3.2.1 stack 이용
1function solution(s) {2const stack = []34// for of : 배열 순회5for (const c of s) {6// 여는 괄호일 경우7if (c === '(') {8stack.push(c)9} else {10// 스택이 비어있는 경우11if (stack.length === 0) {12return false13}14// 닫는 괄호일 경우15stack.pop()16}17}18// 빈 배열이라면 true, 아니라면 false19return stack.length === 020}
3.2.2 stack을 이용하지 않는 방법
stack보다 메모리를 적게 사용 가능
1function solution(s) {2let opened = 03for (const bracket of s) {4if (bracket === '(') opened += 15if (bracket === ')') opened -= 16if (opened < 0) return false7}8return opened === 09}